Abstract
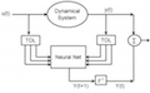
A single biological neuron is able to perform complex computations that are highly nonlinear in nature, adaptive, and superior to the perceptron model. A neuron is essentially a nonlinear dynamical system. Its state depends on the interactions among its previous states, its intrinsic properties, and the synaptic input it receives. These factors are included in Hodgkin-Huxley (HH) model, which describes the ionic mechanisms involved in the generation of an action potential. This paper proposes training of an artificial neural network to identify and model the physiological properties of a biological neuron, and mimic its input-output mapping. An HH simulator was implemented to generate the training data. The proposed model was able to mimic and predict the dynamic behavior of the HH simulator under novel stimulation conditions; hence, it can be used to extract the dynamics (in vivo or in vitro) of a neuron without any prior knowledge of its physiology. Such a model can in turn be used as a tool for controlling a neuron in order to study its dynamics for further analysis.