Abstract
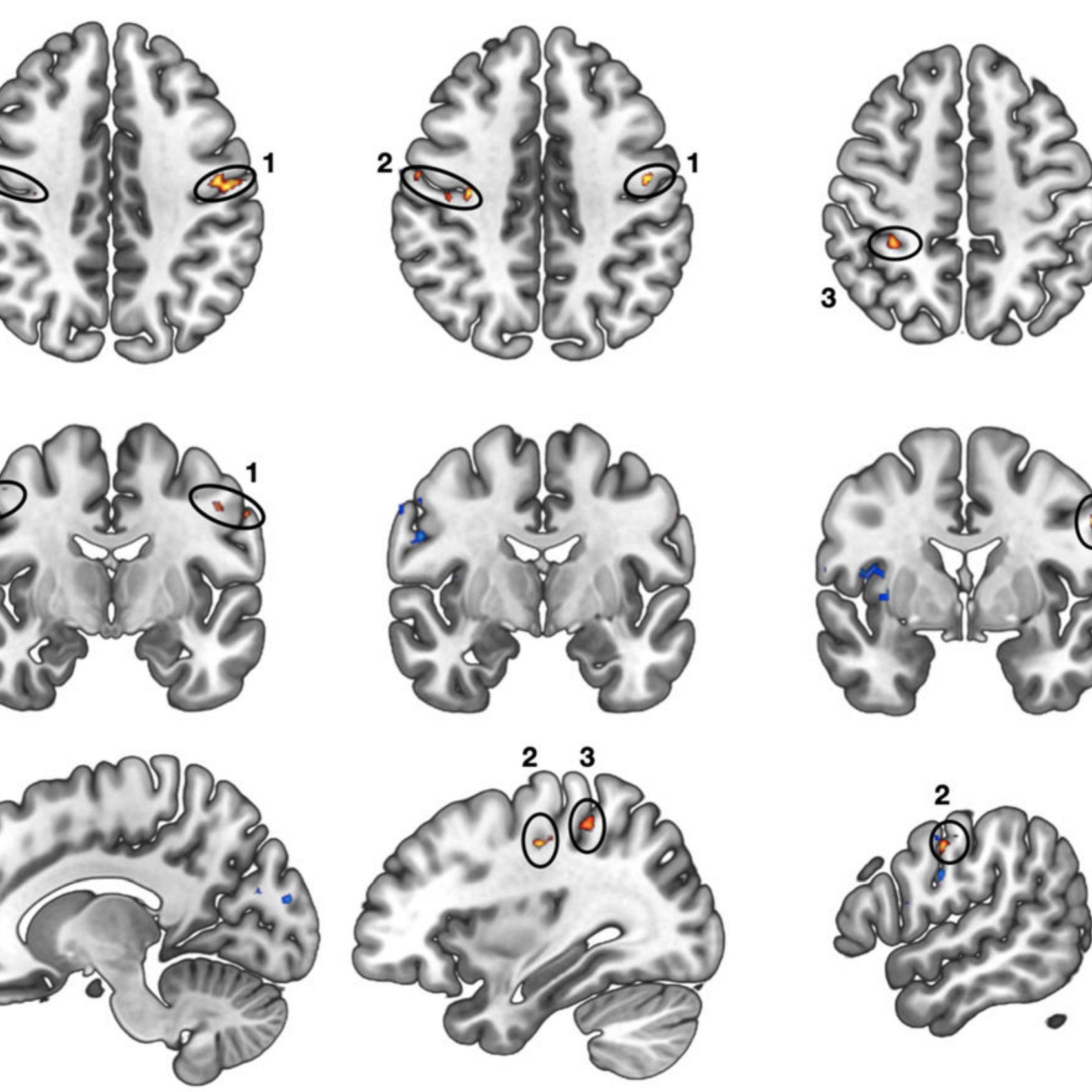
Alterations in sensorimotor functions are common in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Such aberrations suggest the involvement of the thalamus due to its key role in modulating sensorimotor signaling in the cortex. Although previous research has linked atypical thalamocortical connectivity with ASD, investigations of this association in high-functioning adults with autism spectrum disorder (HFASD) are lacking. Here, for the first time, we investigated the resting-state functional connectivity of the thalamus, medial prefrontal, posterior cingulate, and left dorsolateral prefrontal cortices and its association with symptom severity in two matched cohorts of HFASD. The principal cohort consisted of 23 HFASD (mean[SD] 27.1[8.9] years, 39.1% female) and 20 age- and sex-matched typically developing controls (25.1[7.2] years, 30.0% female). The secondary cohort was a subset of the ABIDE database consisting of 58 HFASD (25.4[7.8] years, 37.9% female) and 51 typically developing controls (24.4[6.7] years, 39.2% female). Using seed-based connectivity analysis, between-group differences were revealed as hyperconnectivity in HFASD in the principal cohort between the right thalamus and bilateral precentral/postcentral gyri and between the right thalamus and the right superior parietal lobule. The former was associated with autism-spectrum quotient in a sex-specific manner, and was further validated in the secondary ABIDE cohort. Altogether, we present converging evidence for thalamocortical hyperconnectivity in HFASD that is associated with symptom severity. Our results fill an important knowledge gap regarding atypical thalamocortical connectivity in HFASD, previously only reported in younger cohorts.